Tooth Fairy? NOT IF EMS HAS ANYTHING TO SAY ABOUT IT.
Kidding. The prehospital protocol for the avulsed tooth applies solely to permanent teeth. If encountered, EMTs and paramedics will gently clean the tooth with saline and reimplant it within the socket (assuming the patient isn’t at risk for aspirating the tooth – see the Key Points section). If the patient is not eligible for reimplantation, EMS will prevent the tooth from drying out by placing it in an storage medium – remember that preference is “commercial tooth preservation media” (generic term for Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution) > milk > saliva > saline.
That’s all there is to it! All neatly packaged for you to manage in the ED! Or, more likely, to have the dentist manage! High five!
www.nycremsco.org or the protocol binder for more!
Dave
- Medications
- Pharmacology
- Respiratory / Pulm
- POCUS
- Infectious Disease
- Ophthalmology
- Airway
- Obstetrics / Gynecology
- Environmental
- Procedures
- Foreign Body
- Pediatrics
- Cardiovascular
- EKG
- Critical Care
- Radiology
- Emergency
- Admin
- Orthopedics
- Nerve Blocks
- DVT
- Finance
- EMS
- Benzodiazepines
- Neurology
- Medical Legal
- Psychiatry
- Anal Fissure
- Hemorroids
- Bupivacaine
- Ropivacaine
- EM
- Neck Trauma
- Emergency Medicine
- Maisonneuve Fracture
- Diverticulitis
- Corneal Foreign Body
- Gabapentin
- Lethal Analgesic Dyad
- Opioids
- Galea Laceration
- Dialysis Catheter
- Second Victim Syndrome
- Nasal Septal Hematoma
- Nephrology / Renal
- Hematology / Oncology
- Dental / ENT
- Dermatology
- Endocrine
- Gastroenterology
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- May 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
Dental Trauma
Dental Trauma
Pulp – inner layer with neurovascular supply
Dentin – most of tooth under enamel
Enamel – thin outer layer
Cementum – outer layer of root surface
Crown – visible part of tooth
Root – part not visible covered by cementum
Primary/pediatric teeth – 20 teeth, 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 molars, central incisors start at 7 months of age, 20 by 3 years of age (named A->T)
Permanent Teeth – 32 permanent teeth (8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars, 12 molars), rerupt at 6-7 yo and all 32 by 13 yo
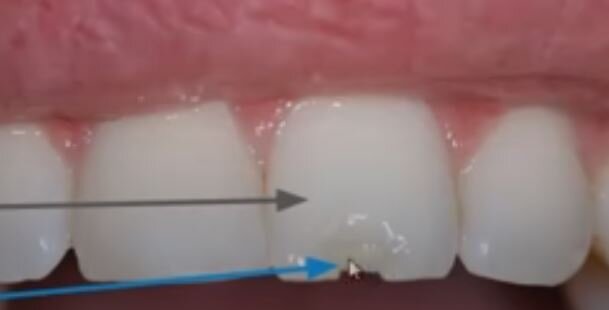
Fracture – evaluate for tooth mobility, sensitivity, fracture
Ellis class I: fracture of enamel, tooth is painless, superficial fracture, no intervention needed, refer to dentistry
Ellis Class II: dentin fracture, dentin which is has soft golden yellow appearance can be seen, this has higher risk of pulp necrosis/infection, needs f/u with dentistry within 24h, consider dental block for pain relief, CaOH sealant
CaOH paste comes in 2 tubes that need to be mixed then spread over the tooth after it has been dried off (have patient bite down on gauze or soak gauze with epinephrine)
Ellis III: pulp exposure which is a dental emergency, usually very painful unclear neurovascular damage, if pink or bloody discharge at fracture surface, need emergent dental evaluation in ED, high risk of abscess formation
Cover with CaOH, likely will need root canal by dentistry
Subluxation – tooth is mobile but not displaced, conservative management w/ soft diet and dental f/u
Luxation – tooth is partially displaced from socket, need tooth splinting for 2-4 weeks, need emergent dental consult
Intrusion – tooth displaced apically, if deep > 3 mm, needs emergent dentistry for repositioning and stabilization, if < 3mm, needs urgent 24h dental f/u
Consider CTH w/ face for boney fracture, consider CXR for aspiration, XR
Complete Avulsion – loss of entire tooth from socket, dental emergency
1. when did trauma occur – each minute tooth is out reduces viability by 1%, ideally reposition in 15-30 min
2. where is tooth? Aspirated (CXR), swallowed, embedded in oral mucosa, if you have the tooth, touch only the crown, rinse with water and ideally keep the tooth in the socket
Store tooth in saliva (mouth), milk, saline (less ideal)
3. is tooth primary/permanent
primary tooth should not be re-implanted, needs dental f/u
permanent tooth needs emergent dentistry, periodontal ligament cells can die within 60 min the tooth is outside oral cavity, reimplant tooth to preserve periodontal ligament – splint until definitive management
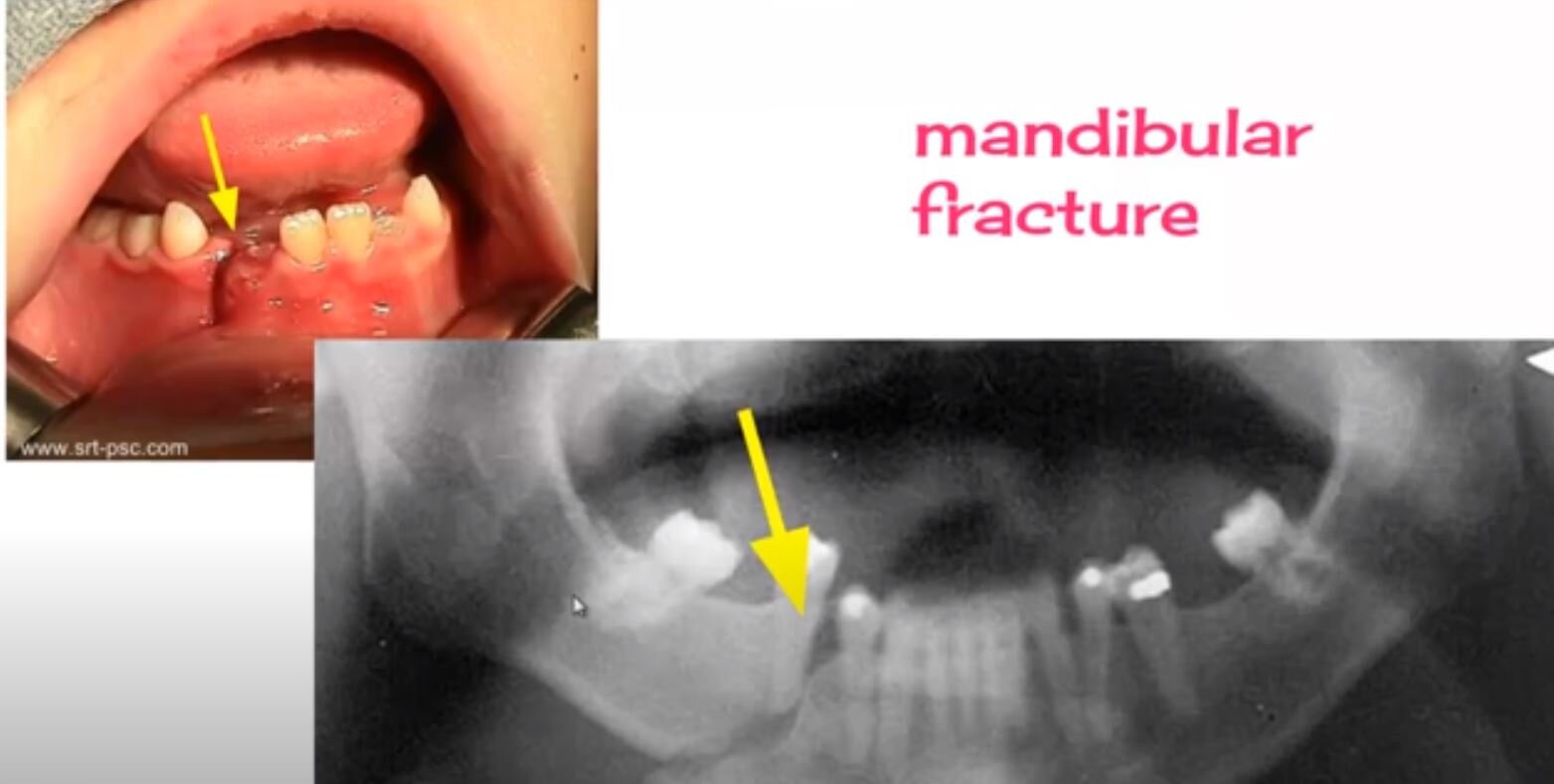
Look for mandibular fracture – can pt open mouth normally, tongue blade test (can pt keep mouth closed to break a tongue blade when twisted), is there pre-auricular tenderness, hematoma at floor of mouth