It’s In-Service season, people! Let’s review the essentials of carbon monoxide poisoning. And before you start with your “Ugh, really? How many times do we have to—“, let me cut you off and have you gimme the full list of indications for hyperbaric oxygen therapy…. EXACTLY. Are you ready to review now?
1) How do these patients present?
HISTORY, HISTORY, HISTORY. The classic example goes something like: A family of five presents from home in the dead of winter complaining of headaches associated with a myriad of vague, nonspecific complaints.

Later on, you overhear mom mention, out of frustration, that she had to pay for an Uber XL to get the whole fam to the ED tonight, since dad’s Camero was ‘on empty.’ Turns out, upon arriving home from the bars last night, dad accidentally left his car keys in the ignition before passing out in the doorway connecting the garage to the kitchen. (Ok, so maybe you won’t see that last part on the boards, but it’s my favorite real-life example).

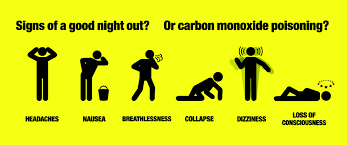
The most common complaints: (1) HEADACHE, (2) nausea, (3) dizziness, and mental status changes with more severe toxicity (memory disturbances commonly manifested as amnesia, decreased cognition, stupor, coma, gait disturbances, etc). Keep in mind that the list of potential associated complaints is broad and encompass nearly every organ system.
Don’t count on the physical exam to nail the diagnosis. Remember that pulse oximetry is not affected. Know the traditional buzz words “cherry red” lips and skin for the boards; but also know that these are rarely seen in clinical practice.
2) How is it diagnosed?
Send a co-oximetry panel. Don’t get tripped up on details- you can send either a venous or arterial blood sample. If your clinical suspicion is high, do not delay treatment pending results.
A CO level >3% in non-smokers, or >10% in smokers, is diagnostic.
The actual percentages weakly correlate with associated symptoms and overall prognosis. That being said, in the proper clinical setting, you can make the diagnosis and treat presumptively with normal or borderline CO levels.
3) How is it treated?
ABC’s- Intubate if the patient is altered and unable to protect his/her airway. Administer 100% oxygen via NRB. Keep this patient on a cardiac monitor. If for no other reason, CO binds to cardiac myoglobin with an even greater affinity than to hemoglobin, resulting in cardiac ischemia, ventricular arrhythmias, and cardiovascular collapse in severe cases. Finally, know your indications for Hyperbaric Oxygen (HBO).**
**note: this list is variable (and debatable) depending on the source, but generally accepted indications include: anyone who is pregnant, anyone who has signs of cardiac ischemia, history of prolonged LOC, or presence of neurological deficits.
- Focal neurological deficits, coma, h/o transient LOC (transient LOC = independent risk factor for increased morbidity)
- Pregnancy (with CO > 15%)
- Evidence of cardiac ischemia, usually on EKG (or h/o CAD with CO >20%)
- Basically any symptoms with CO >40%
- Symptoms that don’t resolve after 6 hrs of 100% O2 via NRB

KEEP IN MIND: Clearance of CO via:
Room air: ~300 minutes
100% NRB: ~90 minutes
HBO: ~15-30 minutes
IDEALLY, TRANSFER FOR HBO SHOULD BE MADE ON A CASE-BY-CASE BASIS, AND SHOULD TAKE INTO CONSIDERATION THE STABILITY OF THE PATIENT FOR TRANSFER AND THE TIME INVOLVED FOR THE TRANSFER PROCESS ITSELF, AMONG OTHER THINGS.
The reason we transfer patients for HBO therapy = prevention of long-term neurologic sequelae.
Want to learn more?
https://lifeinthefastlane.com/ccc/carbon-monoxide-poisoning/
https://lifeinthefastlane.com/ccc/hyperbaric-oxygen-and-carbon-monoxide-poisoning/
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/819987-treatment#d12
https://emcrit.org/racc/cardiac-arrest-after-smoke-inhalation/
SaveSave


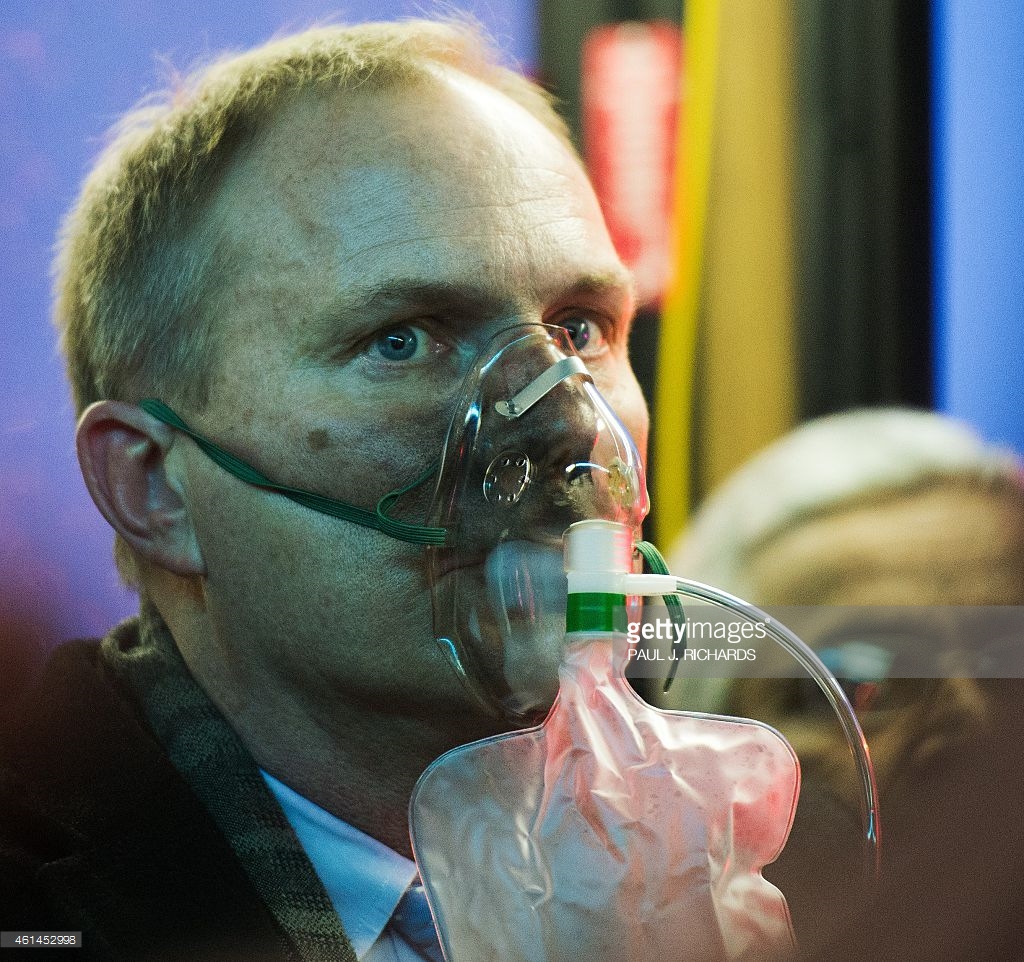
 Nyquil, Tylenol, and Benadryl) are heavily regulated by the Food & Drug Administration (FDA). This regulation generally scrutinizes the benefits/harms the drug had in clinical trials and the manufacturing process, including raw ingredient inspections. Unfortunately, this same oversight doesn’t apply to natural products such as vitamins, minerals, and herbal supplements. There is less scrutiny on manufacturers which may increase the risk of impurities and contamination. This is why it’s always important to pick a “major/recognizable” natural product brands instead of “no-name” generic brands. Natural products are not legally considered “drugs”; instead they’re considered “dietary supplements.” The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994 (DSHEA 1994) prevents natural products from making any health claims, but they are permitted to use phrases such as “supports heart and energy function.” Many of these supplements have the same side effects and drug interactions as prescription medications (since many are derived from the same source), but they can be purchased by anyone without healthcare provider oversight. Nonetheless, there is great potential for these products if they’re utilized under proper medical supervision. Let us take a look at three agents that “support heart health.”
Nyquil, Tylenol, and Benadryl) are heavily regulated by the Food & Drug Administration (FDA). This regulation generally scrutinizes the benefits/harms the drug had in clinical trials and the manufacturing process, including raw ingredient inspections. Unfortunately, this same oversight doesn’t apply to natural products such as vitamins, minerals, and herbal supplements. There is less scrutiny on manufacturers which may increase the risk of impurities and contamination. This is why it’s always important to pick a “major/recognizable” natural product brands instead of “no-name” generic brands. Natural products are not legally considered “drugs”; instead they’re considered “dietary supplements.” The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994 (DSHEA 1994) prevents natural products from making any health claims, but they are permitted to use phrases such as “supports heart and energy function.” Many of these supplements have the same side effects and drug interactions as prescription medications (since many are derived from the same source), but they can be purchased by anyone without healthcare provider oversight. Nonetheless, there is great potential for these products if they’re utilized under proper medical supervision. Let us take a look at three agents that “support heart health.”