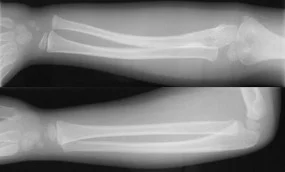
TRAUMA TUESDAY POD- ARTERIAL PRESSURE INDEX
INDICATIONS
Severe extremity injury with...
Proximity of injury to vascular structures
Major single nerve deficit
Reduced pulses
Posterior knee or anterior elbow dislocation
Hypotension or moderate blood loss at scene
Concern for vascular injury
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Unable to place BP Cuff around ankle or arm due to injury
EQUIPMENT
Manual BP Cuff
Handheld Doppler Instrument
Ultrasound Gel
PROCEDURE
Measure systolic pressure in injured extremity distal to the injury (may measure radial, ulnar, brachial, dorsalis pedis, posterior tibial)
Measure systolic pressure in uninjured brachial artery
Perform Calculation: Injured extremity SBP/ Uninjured brachial SBP
INTERPRETATION
API >0.9: Vascular injury very unlikely, CT angio unnecessary
API <0.9: Possible vascular injury, CT angio is indicated