Understanding EKG Patterns
- Medications
- Pharmacology
- Respiratory / Pulm
- POCUS
- Infectious Disease
- Ophthalmology
- Airway
- Obstetrics / Gynecology
- Environmental
- Procedures
- Foreign Body
- Pediatrics
- Cardiovascular
- EKG
- Critical Care
- Radiology
- Emergency
- Admin
- Orthopedics
- Nerve Blocks
- DVT
- Finance
- EMS
- Benzodiazepines
- Neurology
- Medical Legal
- Psychiatry
- Anal Fissure
- Hemorroids
- Bupivacaine
- Ropivacaine
- EM
- Neck Trauma
- Emergency Medicine
- Maisonneuve Fracture
- Diverticulitis
- Corneal Foreign Body
- Gabapentin
- Lethal Analgesic Dyad
- Opioids
- Galea Laceration
- Dialysis Catheter
- Second Victim Syndrome
- Nasal Septal Hematoma
- Nephrology / Renal
- Hematology / Oncology
- Dental / ENT
- Dermatology
- Endocrine
- Gastroenterology
- July 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- May 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
Pearl of the day - Nebulized Analgesia
To paraphrase Dr. Sergey Motov: when IV access is unattainable or undesirable, nebulized, intranasal and transmucosal administration of analgesics should be considered for acute pain management in the ED. The best evidence is from a systematic review of nebulized fentanyl (see citation).
The doses (off-label use) are: 4mcg/kg for an adult titrated up to three doses. Peds: 2-4mcg/kg. For morphine: 0.2mg/kg peds, 10mg or 20mg adults fixed-dose.
We can use the breath-actuated nebulizer (pic) to ensure patient-controlled dosing. It is located in the pyxis or from pharmacy. If you still don’t know how to use it, ask!
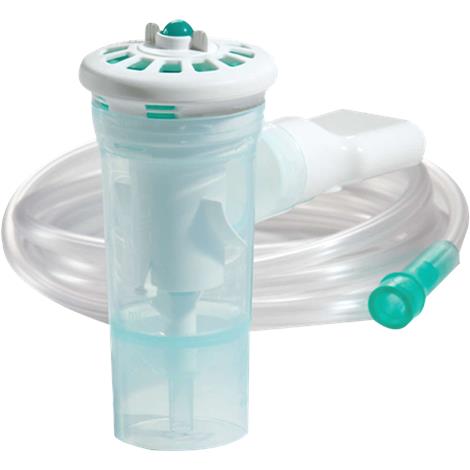
Manufacturer video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7Xk-tYhhEdU
See this article for more information:
Thompson JP, Thompson DF. Nebulized Fentanyl in Acute Pain: A Systematic Review. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2016, Vol 50(10): 882-891.
Rapid Board-Style Review of Orthopedic Injuries to the Foot/Ankle
SALTER HARRIS I -> S-slipped -> non-op
II -> A-Above physis (through metaphysis) -> non-op
III -> L-Lower than physis (through epiphysis) -> unstable
IV ->T-Throuh physis (all 3 involved) ->limb-length discrepancy->Op
V ->R-ERasure of growth plate (crush) -> Op
ANKLE/FOOT injuries.
▪Achilles tendon rupture – weekend warriors, cipro use, -> + Thompson test – no plantar flexion w/ calf compression -> splint in equine position, ortho eval.
▪Ottawa ankle rules – pain at posterior edge of either malleoli, inability to bear weight immediately/in ED. Navicular TTP, TTP at base of 5th metatarsal
▪Weber ankle fractures -> unstable fractures are types B/C at or below the ankle joint -> OR
▪Trimalleolar fx -> OR
▪Maisonneuve fx – Eversion injury -> proximal fibula fx + medial malleolus fx + disruption of syndesmosis
▪Plafond or pilon fx – comminuted distal tibia -> look for associated injuries
▪Calcaneus fx – most common tarsal bone fx <20 degrees Bohler’s angle -> look for associated injuries such as vertebrae
▪Talus bone is most susceptible foot bone to AVN (also scaphoid, odontoid, femoral head)
▪ATFL (ligament) – Inversion injury (most common ankle sprain).

▪ (left pic) Jones fx -> 5th metatarsal shaft fx -> NWB -> Op
▪(right pic) Pseudojones fx -> 5th metatarsal avulsion fx -> hard sole shoe -> most non-op
▪Tarsal tunnel syndrome -> posterior tibial N neuropathy -> weak flexors, pain on sole of foot.
▪Morton’s neuroma -> pain between 2nd/3rd toes usually
▪Plantar fasciitis -> worst in morning, better after use. Tx: rest/NSAIDs
▪Lisfranc fx -> Joint between base of 1st, 2nd metatarsals and cuneiform disrupted. Most require OR.
▪Plantar puncture wounds -> staph/strep most common. Pseudomonas concern if punctured through shoe. Abx controversial
